April 2021
28 years old female presented on 5th post partum day with altered sensorium and one episode of seizures. No history of elevated blood pressure. Sodium level at time of admission was 172 mEq/L.
Case contributed by –
Niharika Prasad, MD, Assistant Professor
Dr. D.Y.Patil Medical College, Hospital & Research Center, Pune, India
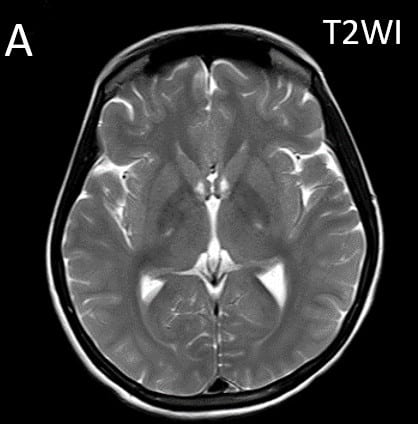
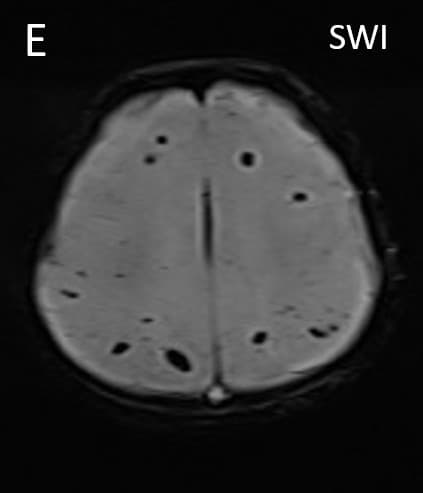
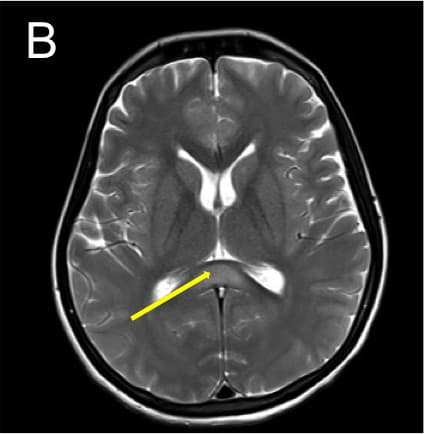
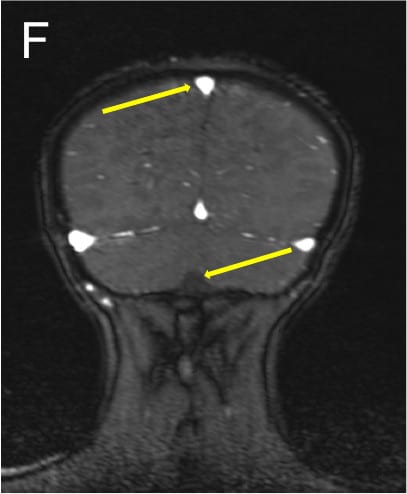
•Axial T2 images (A,B) show hyperintensity in posterior limbs of internal capsules and splenium of corpus callosum with diffusion restriction in splenium (C,D) • •Axial SWI (E) shows few microhemorrhages in both frontal and parietal white matter. •3D TOF venogram (E) shows normal superior sagittal and transverse sinuses. TOF angiogram was unremarkable.
Final Diagnosis- POSTPARTUM HYPERNATREMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY (OSMOTIC MYELINOLYSIS) •Myelinolysis occurring due to hypernatremia in post partum period is uncommon and can occur due to various reasons especially due to ritualistic feeding and dehydration practiced in some communities in India during postpartum period. Often this condition is associated with rhabdomyolysis.
Clinical presentation:
Various neurological manifestations like confusion, seizures, delirium and altered sensorium.
Key diagnostic features:
Bilateral symmetrical T2 and FLAIR hyperintensities involving corpus callosum (especially splenium), corona radiata, internal capsules and cerebral peduncles. These signal changes appear bright on DWI in initial phase.
The “wine glass” appearance on coronal T2 image in classical cases due to involvement of corticospinal tracts.
Although less frequently reported in this cohort of patients, vascular events (infarction and hemorrhage) were not uncommon.
Differential diagnosis •Preeclampsia-Eclampsia: Presentation includes severe headache and visual symptoms with cerebral edema, infarcts and hemorrhage seen on MR imaging. •Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome: Referred to as ‘postpartum angiopathy’ in puerperium. Patients usually present with thunderclap headache. Multifocal constriction of cerebral arteries is seen which resolve within 3 months. Small cortical infarcts following watershed distribution and sub arachnoid hemorrhage may be seen in this condition.
Treatment is correction of hypernatremia with intravenous fluid therapy was achieved within a week with complete recovery by 3 weeks.
References:
1. Chhabra A, Kaushik R, Kaushik RM, Goel D. Extra-pontine myelinolysis secondary to hypernatremia induced by postpartum water restriction. The neuroradiology journal. 2017 Feb;30(1):84-7.
2. Vishwanath SR, Sekhar M, Bele K, Chandrashekar RK. Postpartum hypernatremic cerebral encephalopathy with osmotic myelinolysis: Report of two cases and review with emphasis on magnetic resonance imaging findings. International Journal of Advanced Medical and Health Research. 2015 Jul 1;2(2):112. 3. Bhatia S, Kapoor AK, Sharma A, Gupta R, Kataria S. Cerebral encephalopathy with extrapontine myelinolysis in a case of postpartum hypernatremia. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2014;24(1):57–60









Hemorrhagic PRES
DD- Extrapontine myelinolysis
Hemorrhagic PRES
D/d s
CLOCCs
Marchiafava bignamy .if there is history of alcohalism /malnutrition