September 2021
CASE HISTORY
53 year old female presented with complains of gait imbalance and ataxia.
She has chronic kidney disease and was recently started on anti tubercular therapy (ATT) for pulmonary tuberculosis
Case contributed by –
Dr. Sam K George, Dr. Savith Kumar.
Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences
Apollo hospitals, Bannerghatta -Bangalore
Axial DWI (A), ADC (B), T2WI -axial (C) & FLAIR axial(D ) images shows symmetrical hyperintensities involving bilateral dentate nuclei(white arrows).
Final diagnosis – Isoniazid Induced Neurotoxicity(INH) (Drug induced Cerebellitis).
Neurotoxicity seen in chronic kidney patient taking isoniazid due to reduced clearance of INH.
The mechanism for INH toxicity is due to energy deprivation and deficiency of Vitamin B complex. There is interruption of pathways responsible for pyridoxine phosphorylation resulting in decreased production of pyridoxal 5-phosphate required for neurotransmission via gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Deficiency of GABA results in cerebellar signs.
Pyridoxine supplementation is always advised with INH therapy. However, even with pyridoxine supplementation (15–50 mg/day), up to 5% of patients would still have some adverse effects, with the proportion rising fourfold when pyridoxine dosage is inadequate.
Clinical presentation: INH neurotoxicity can present with seizures, encephalopathy, and peripheral neuropathy. Cerebellar ataxia is rare
Key imaging features: T2 and FLAIR image showing symmetrical hyperintensities involving bilateral dentate nuclei due to its toxicity-induced edema.
Differential diagnosis -Metronidazole toxicity, Enteroviral encephalopathy, Atypical Wernicke’s encephalopathy.
Treatment- Starting patient on pyridoxine and ATT regime need to be modified.
References:
1.Navni Garg, Rahul Mutreja. Bilateral dentate hyperintensities: Isoniazid –induced toxicity European society of Radiology 10.1594/EURORAD/CASE.13907
2. Prashant Peter, Mary John (2014) Isoniazid-induced cerebellitis: a disguised presentation. Singapore Med J 55(1):e17–e19. (PMID: 4291918)
3.S Senthil Raj Kumar, S Shanmuga Jayanthan,G Rupesh (2020) Isoniazid: A rare drug-induced cause for bilateral dentate nuclei hyperintensity. Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging.


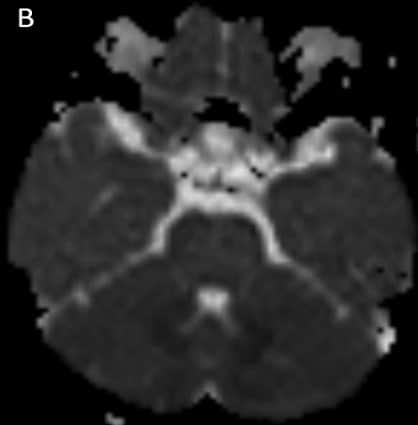
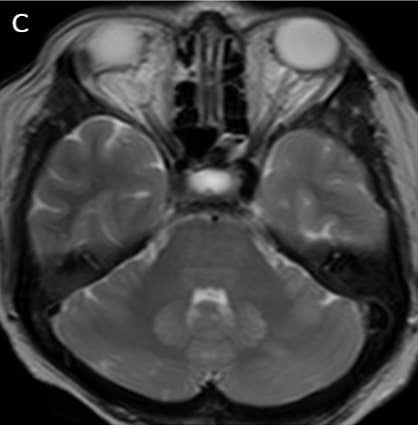

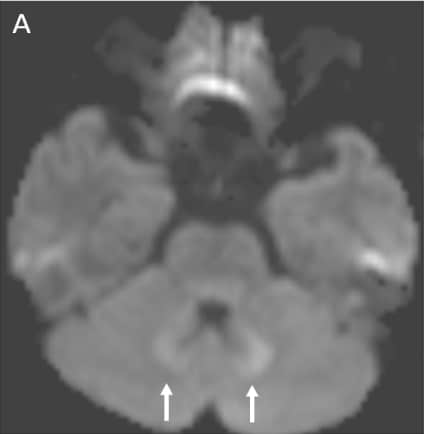

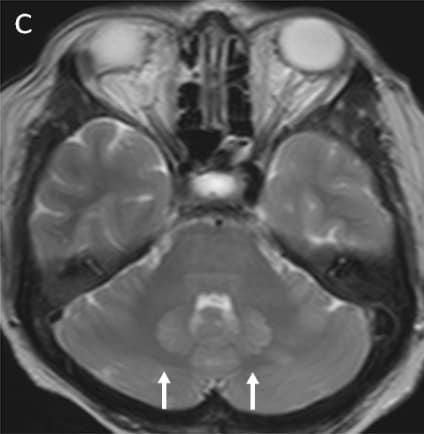

INH toxicity – bilateral symmetrical dentate nucleus hyperintensity
INH toxicity
Drug toxicity isoniazid
INH toxicity
Isoniazid induced toxicity